How to Deploy and Monitor Redis Docker Containers
This guide walks through deploying Redis containers using ServerBuddy's visual interface, covering both basic deployments and production configurations.
Prerequisites
Your Linux server needs:
- Docker or Podman installed
- 256MB+ available RAM
- 5GB+ free disk space
You can check Docker installation by navigating to the "Containers" tab or by running the following in the Terminal:
docker --version
# or
podman --version
Creating a Redis Container with GUI
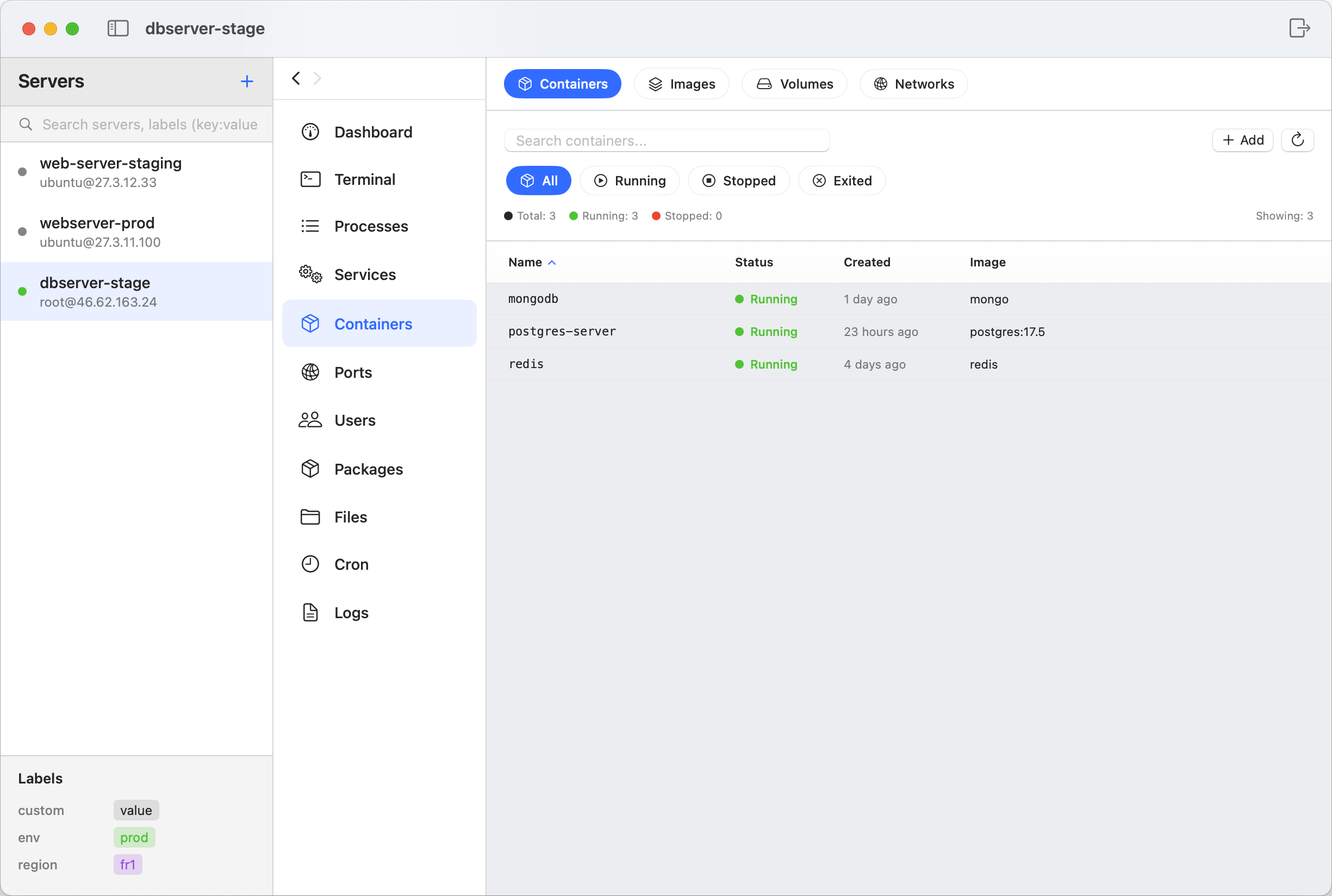
Step 1: Navigate to Docker Management
- Connect to your server via ServerBuddy
- Click the "Containers" tab
Step 2: Configure Container Parameters
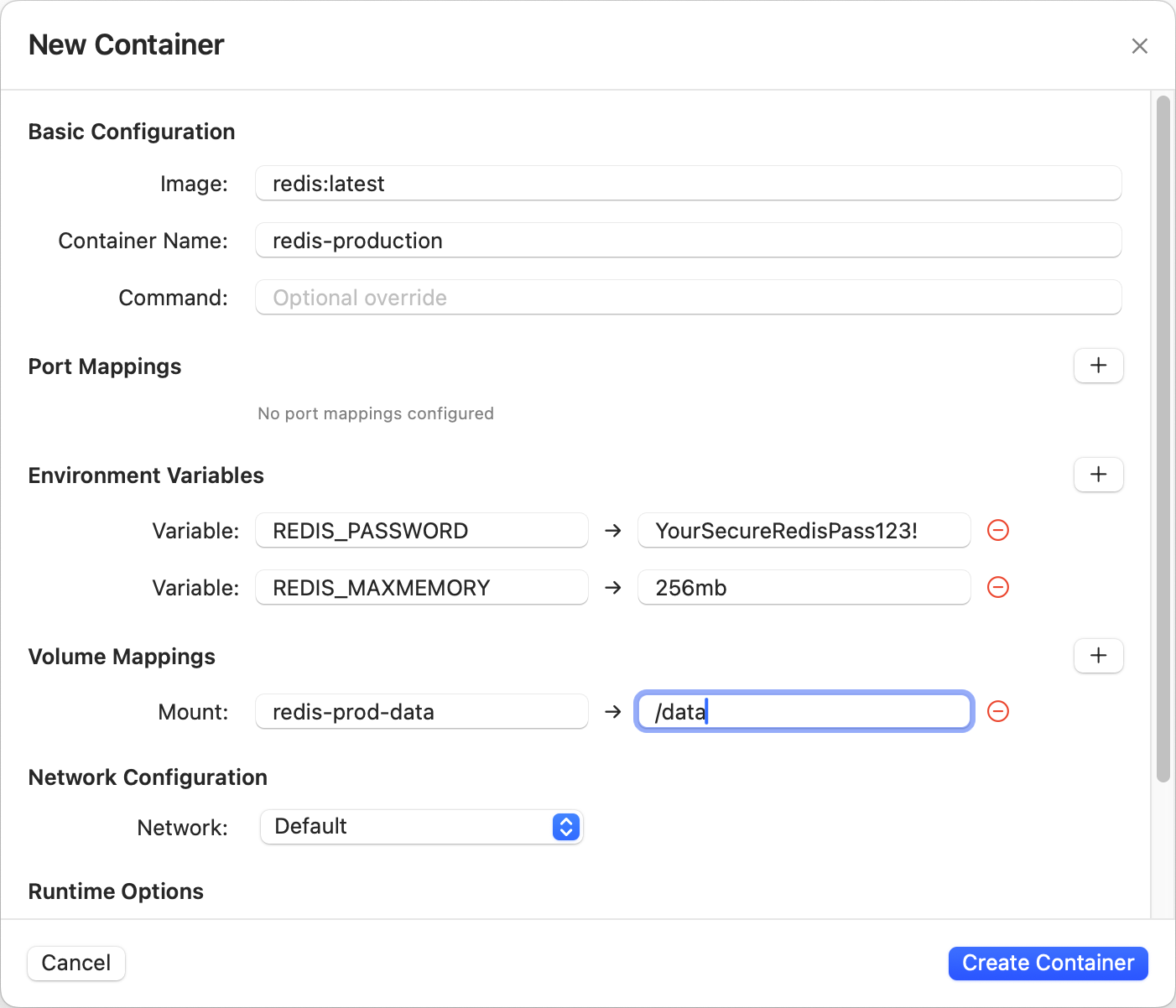
Click the "+ Add" button in the top right to open the container dialog:
Basic Configuration
- Image:
redis:7-alpine(orredis:latestfor newest version) - Container Name:
production-redis(descriptive naming) - Command: Leave empty (uses Redis default entrypoint)
Port Mappings
Enter the following in the port mappings section:
- Host Port:
6379→ Container Port:6379 - Alternative: Use
6380on host if 6379 is occupied
Environment Variables (Optional for Redis)
Add these optional Redis environment variables:
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
REDIS_PASSWORD |
YourSecureRedisPass123! |
REDIS_MAXMEMORY |
256mb |
REDIS_MAXMEMORY_POLICY |
allkeys-lru |
Volume Mappings for Data Persistence
Configure persistent storage to survive container restarts:
- Mount:
redis-production-data(Docker volume name) - Container Path:
/data
This ensures your Redis data persists even if the container is removed.
Network Configuration
- Choose custom network for multi-container applications
- ServerBuddy shows available networks in a dropdown
Runtime Options
- Restart Policy: Select "Unless Stopped" for production
- ✅ Run in detached mode: Keeps container running in background
- ❌ Remove on exit: Keep unchecked for persistent cache
Step 3: Deploy the Container
Click "Create Container" to:
- Pull the Redis image if not present
- Create volume directories
- Start the container with specified configuration
- Display creation status
The container should be running within 5-10 seconds.
Monitoring Redis Container Health
Container Status Indicators
The Docker containers view displays:
Container Status Indicators
- 🟢 Green: Running healthy
- 🟡 Yellow: Starting/restarting
- 🔴 Red: Stopped or errored
- ⚪ Gray: Paused
Available Container Actions
Hover over the container row to access:
- Start/Stop/Restart controls
Checking Redis Performance
Container Resource Usage
You can view this by double clicking on your container entry in the containers table.
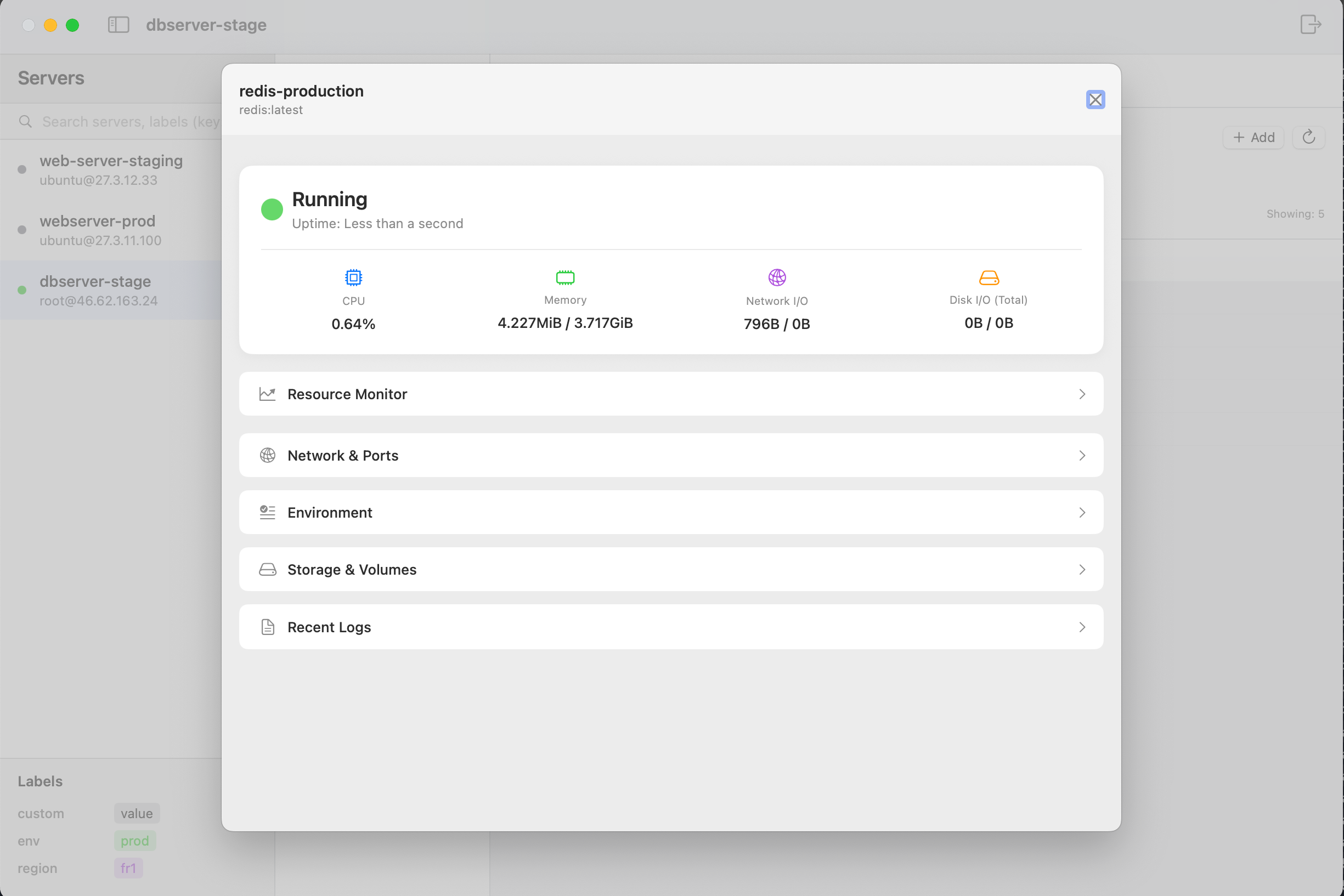
The container details view shows:
- Memory consumption vs. limits
- CPU usage percentage (real-time graph)
- Network I/O rates (inbound/outbound)
- Disk read/write operations
Redis Internal Metrics
Connect via the Terminal tab:
- Click the Terminal tab
- Connect to Redis container
Connect to Redis:
docker exec -it production-redis redis-cli
Run performance queries:
INFO memory
INFO stats
INFO clients
DBSIZE
Log Analysis
You can view the logs for the container in the "Logs" tab by changing the log source to "Containers", and then selecting your container from the dropdown list.
The log viewer offers:
- Filtering by log level (ERROR, WARNING)
- Text search across logs
- Real-time updates
Troubleshooting Connection Issues
If you can't connect to Redis: 1. Check port mapping in container details (default: 6379) 2. Review container logs for authentication errors 3. Verify Redis password configuration if authentication is enabled 4. Confirm firewall rules allow the connection
Security Best Practices
- Enable password authentication with
requirepassdirective - Limit port exposure to specific IPs when possible
- Set memory limits to prevent resource exhaustion
- Disable dangerous commands in production
- Use Redis ACL for granular access control
Common Issues and Solutions
Container Won't Start
- Check logs for error messages
- Verify port availability
- Ensure image exists
- Check volume mount permissions
Connection Refused
- Confirm container is running
- Verify port mapping
- Check firewall rules
- Review Redis authentication settings
Memory Issues
- Set appropriate
maxmemorypolicy - Monitor memory usage regularly
- Configure eviction policies
- Review key expiration settings
Key Takeaways
- Always use volumes for data persistence at
/data - Set specific image tags (e.g., redis:7-alpine) instead of 'latest'
- Configure memory limits to prevent container from consuming all system resources
- Use restart policies for automatic recovery
- Enable persistence with RDB or AOF for critical data